I'll help break this down into SEO-optimized summaries. Let me analyze the content page by page and provide the structured response you requested.
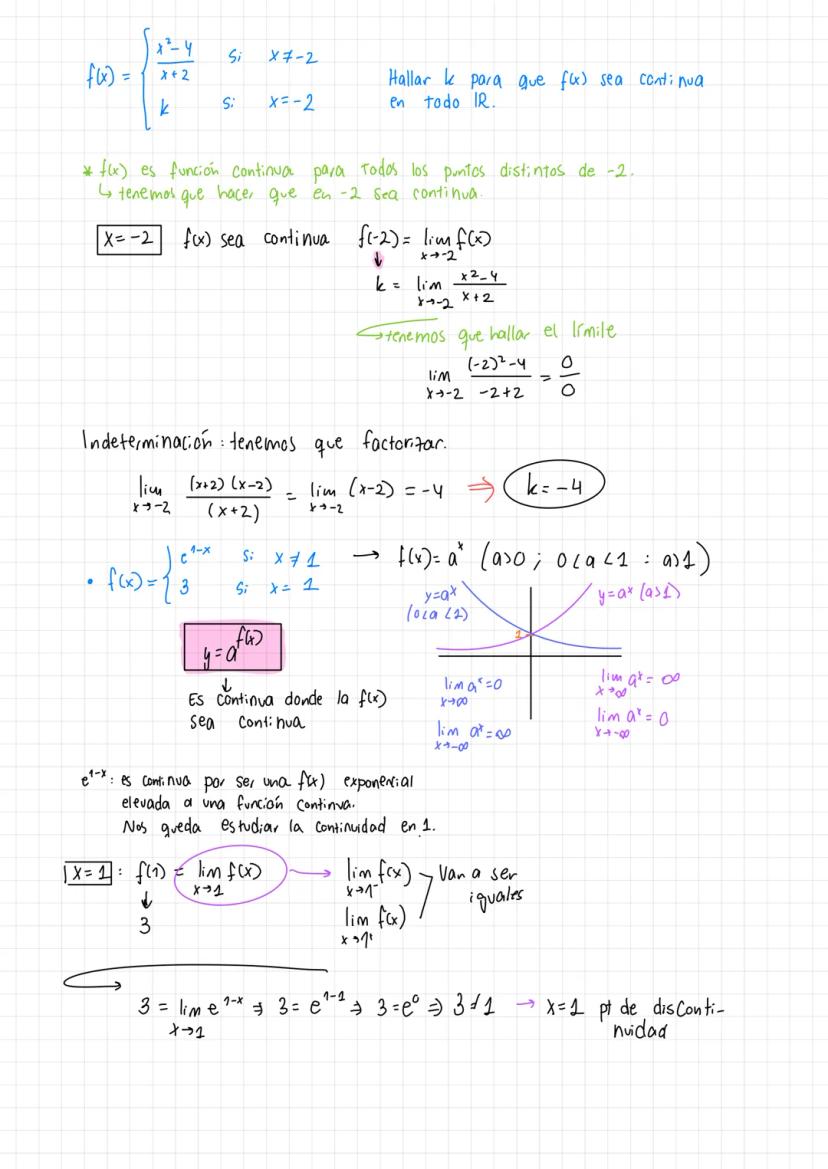
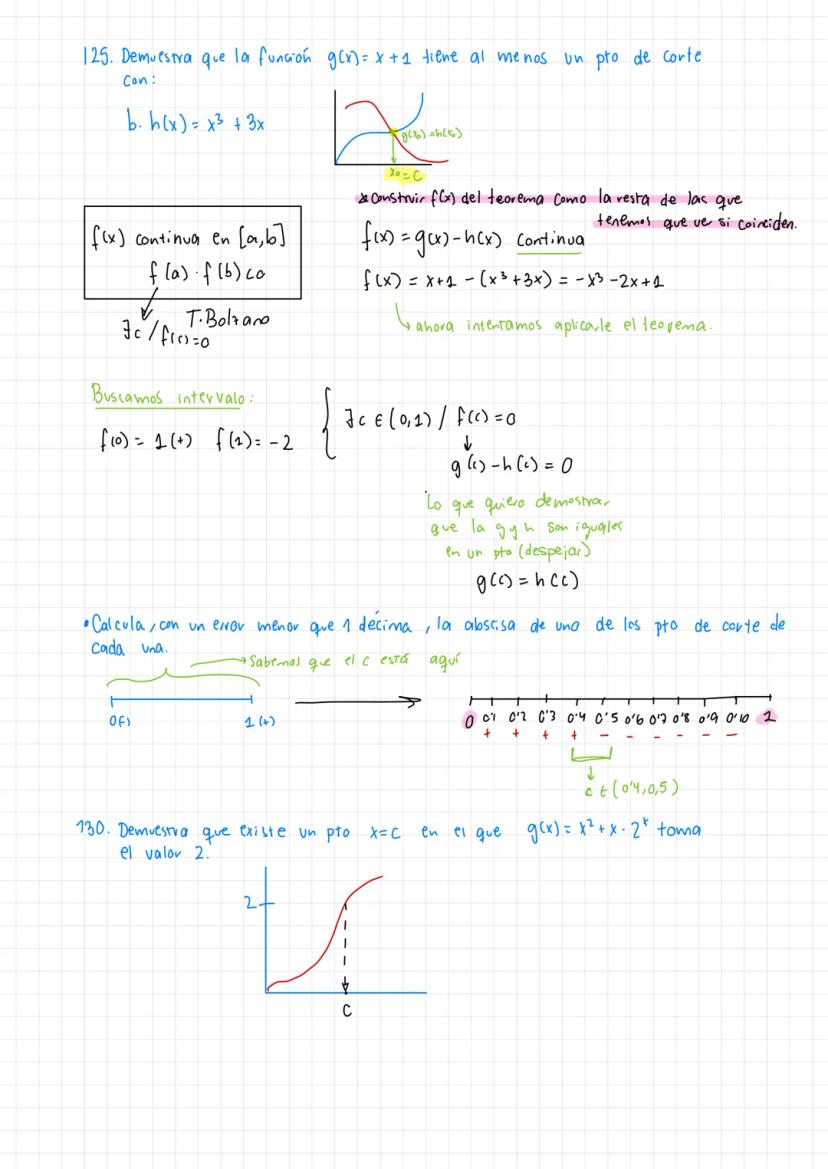
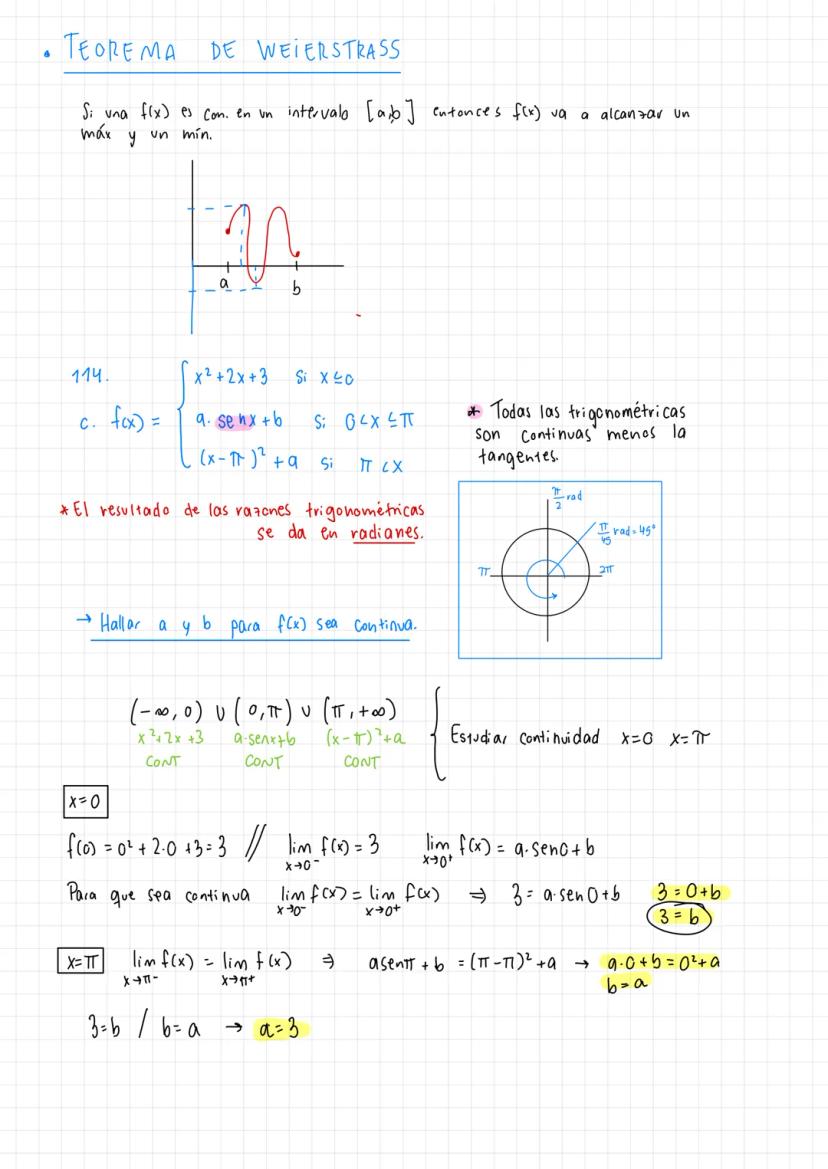
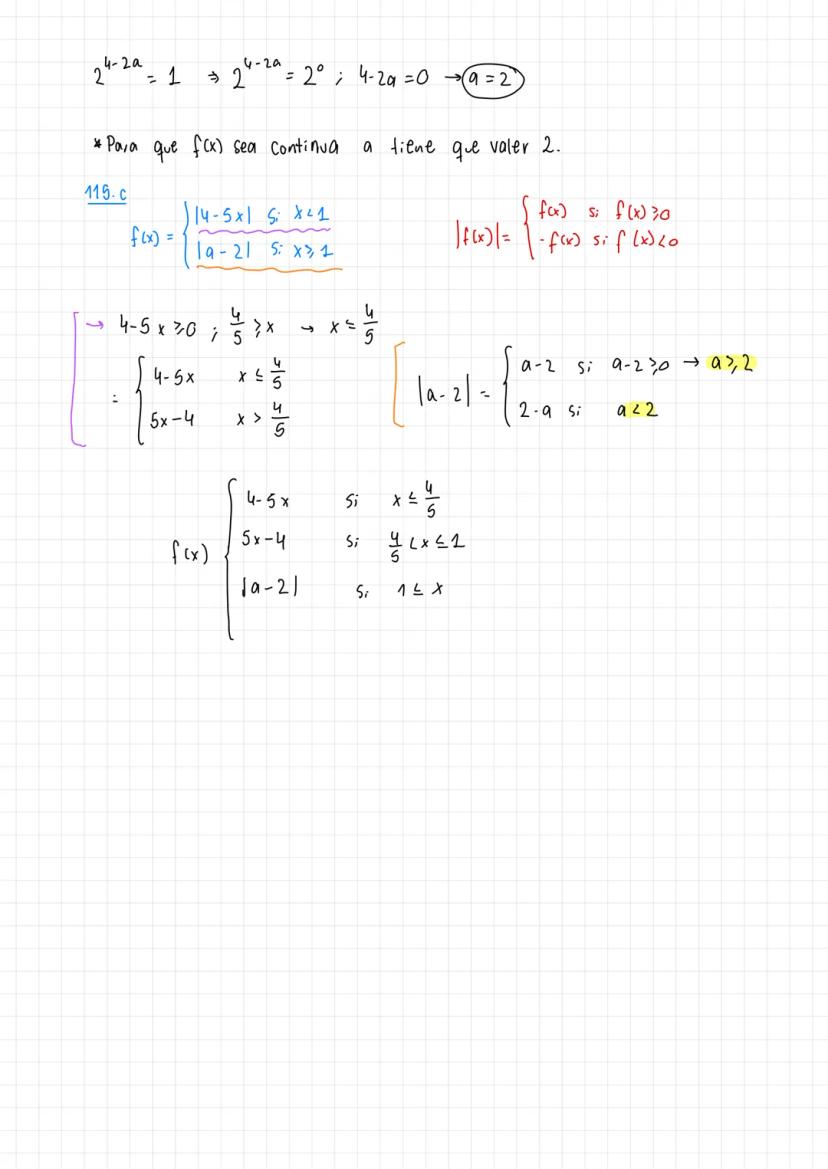
A comprehensive guide to Límites y continuidad and mathematical theorems including the Teorema de Bolzano and function continuity analysis.
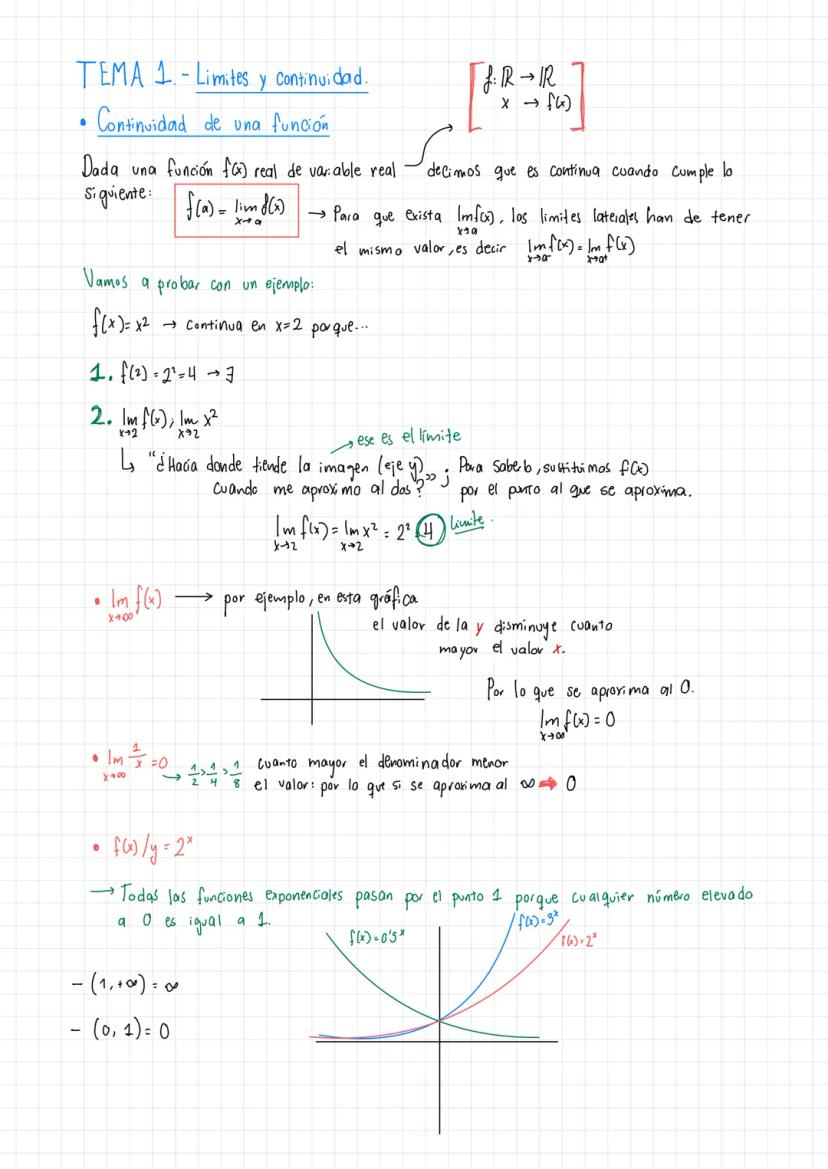
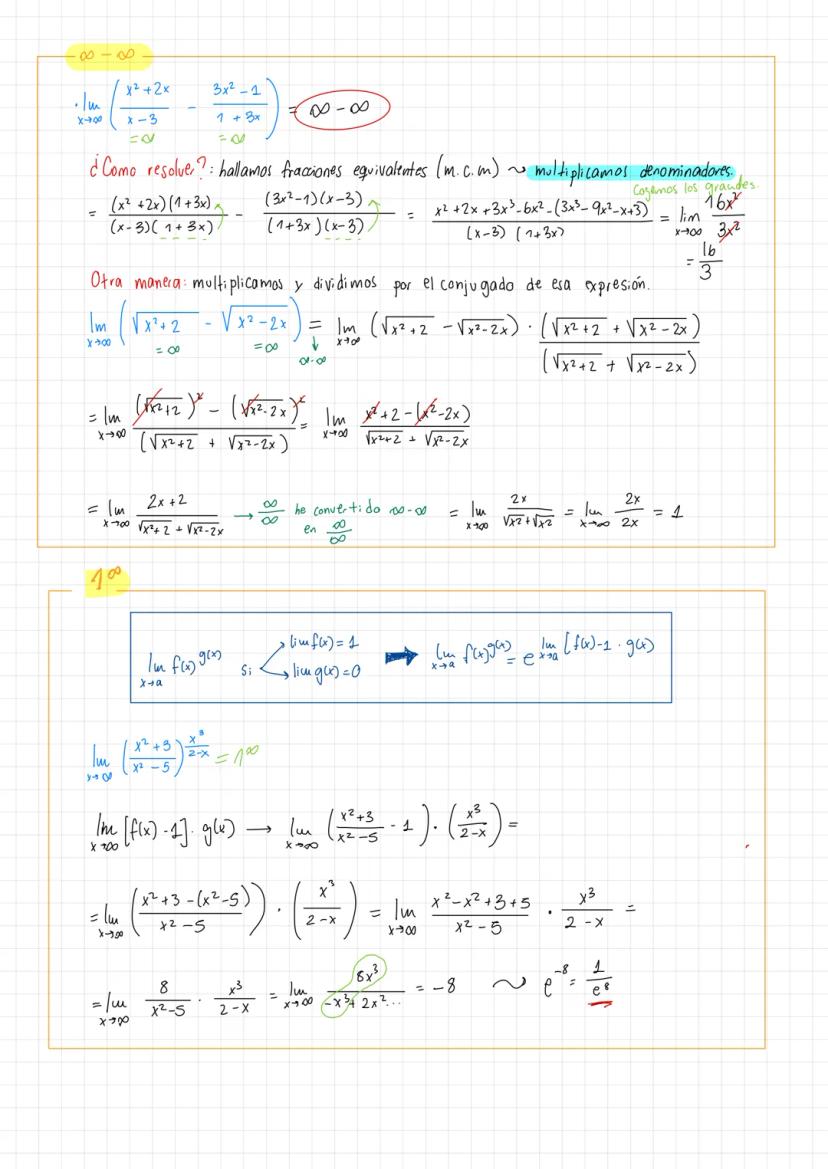
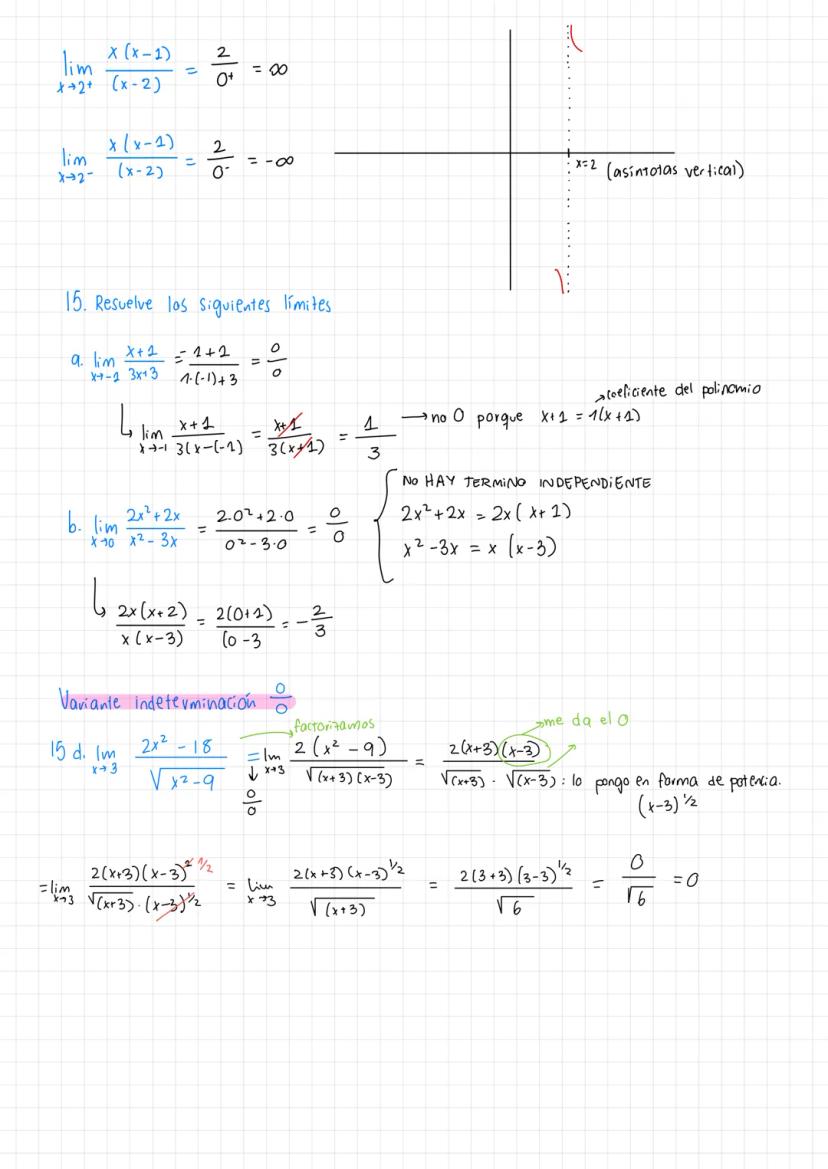
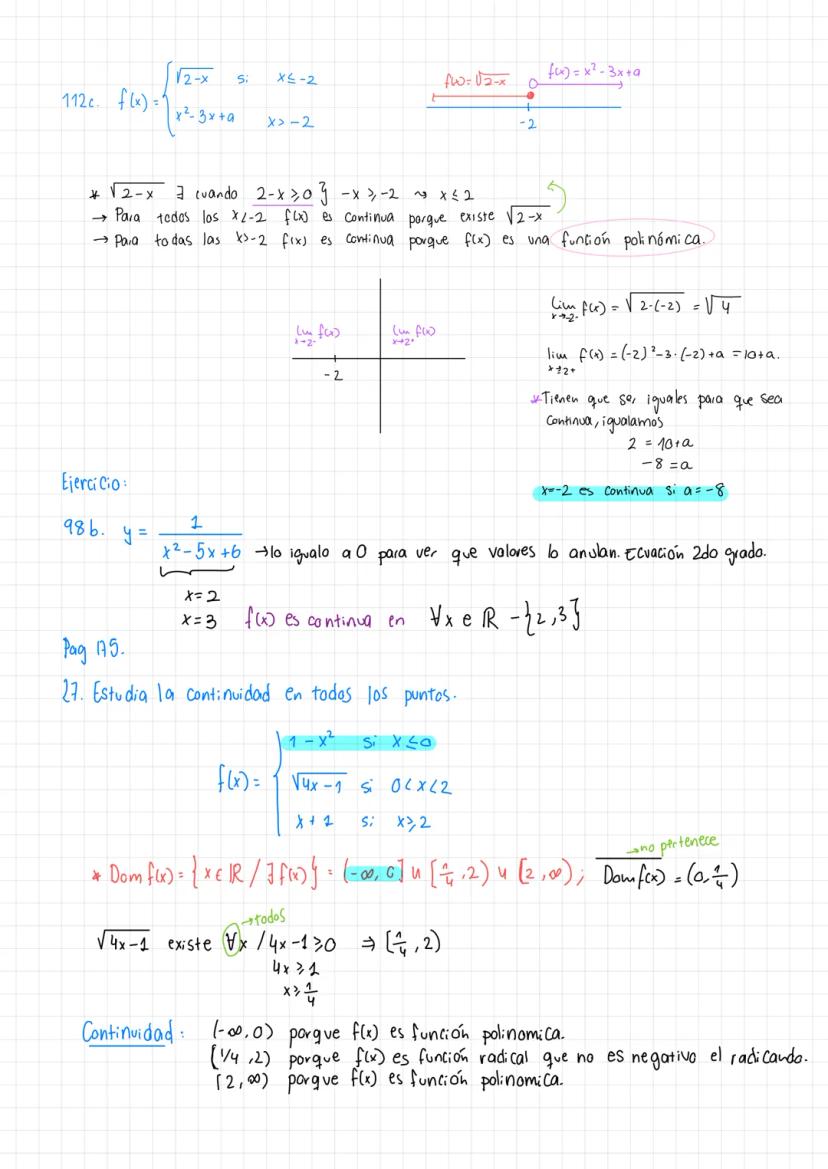
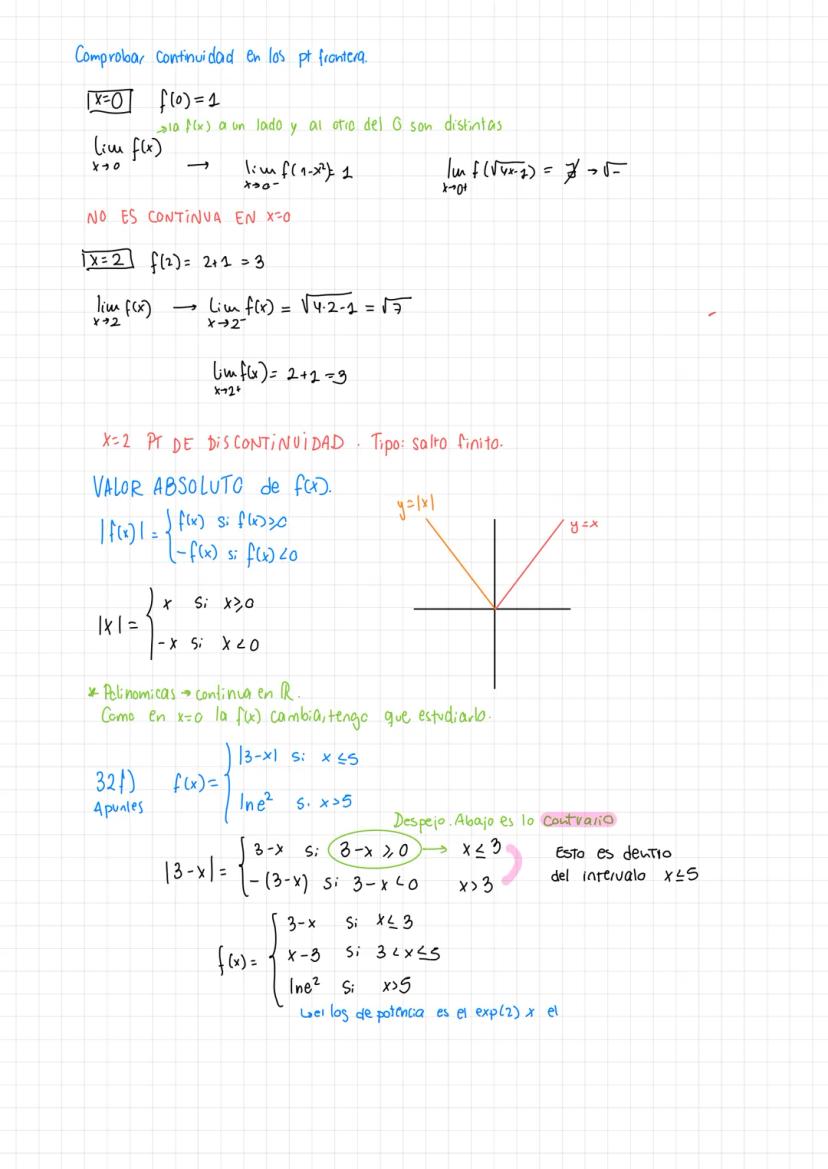
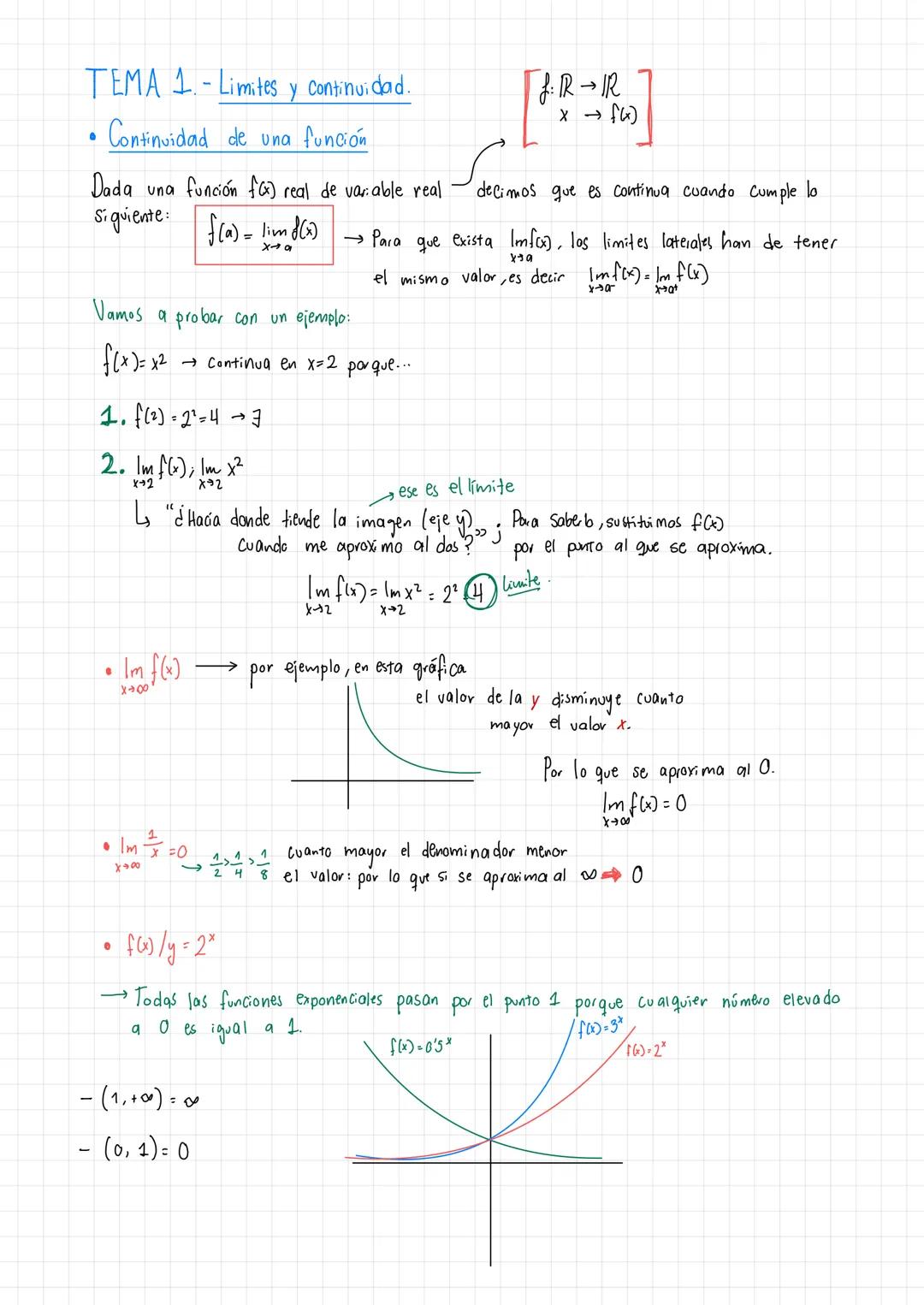
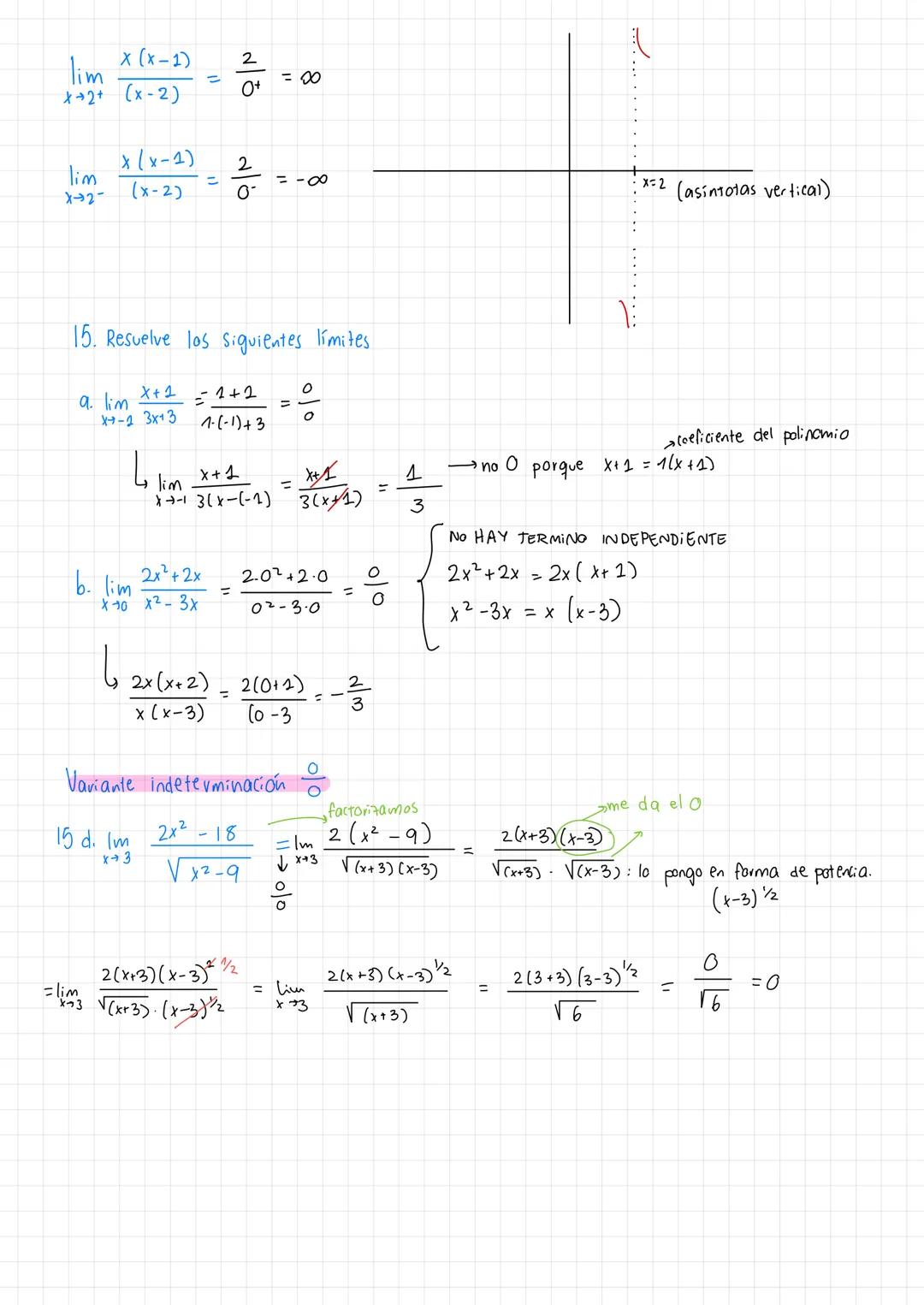
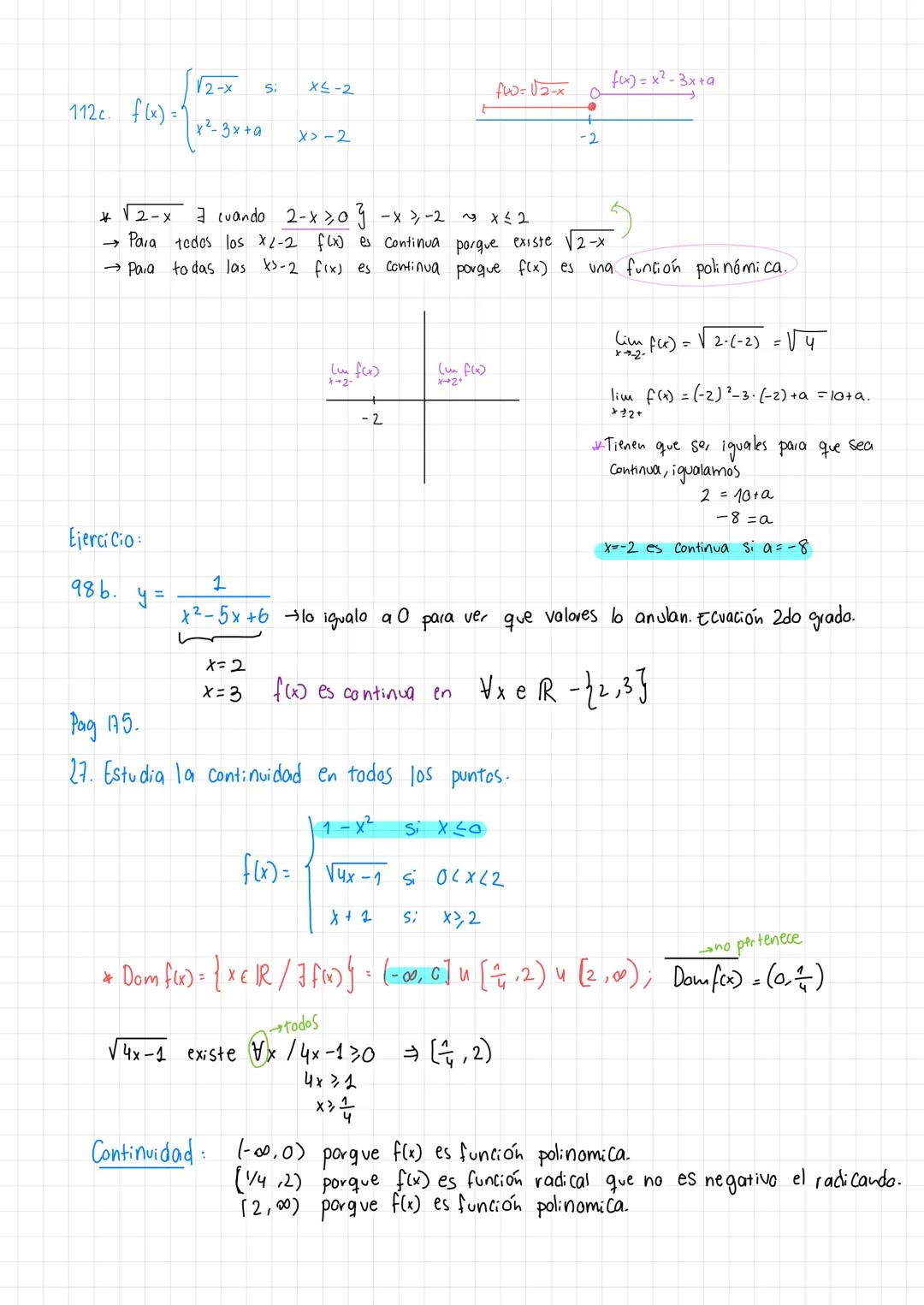
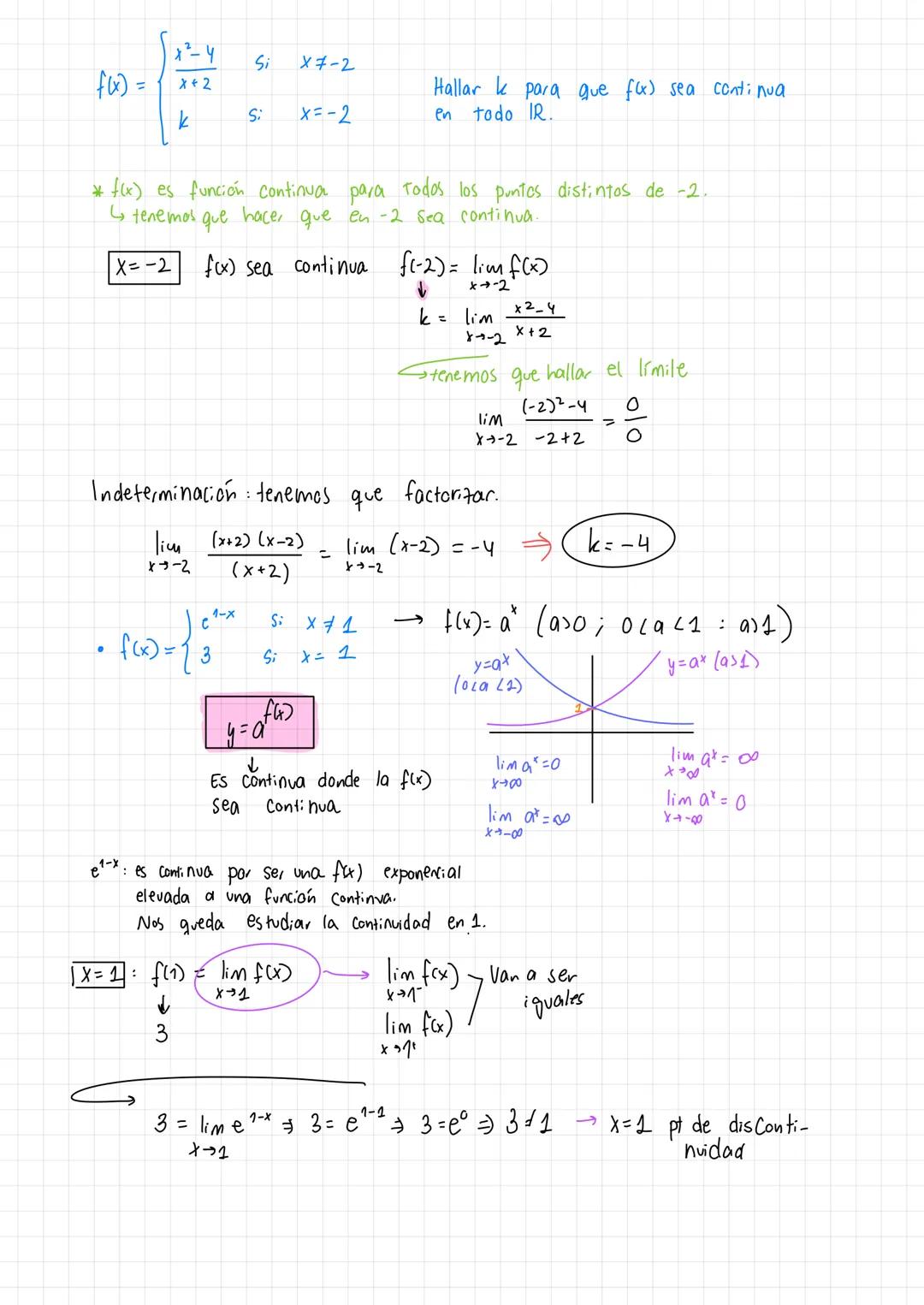
• The material covers essential concepts in calculus including limits, continuity, and important theorems like Teorema de Bolzano-Weierstrass
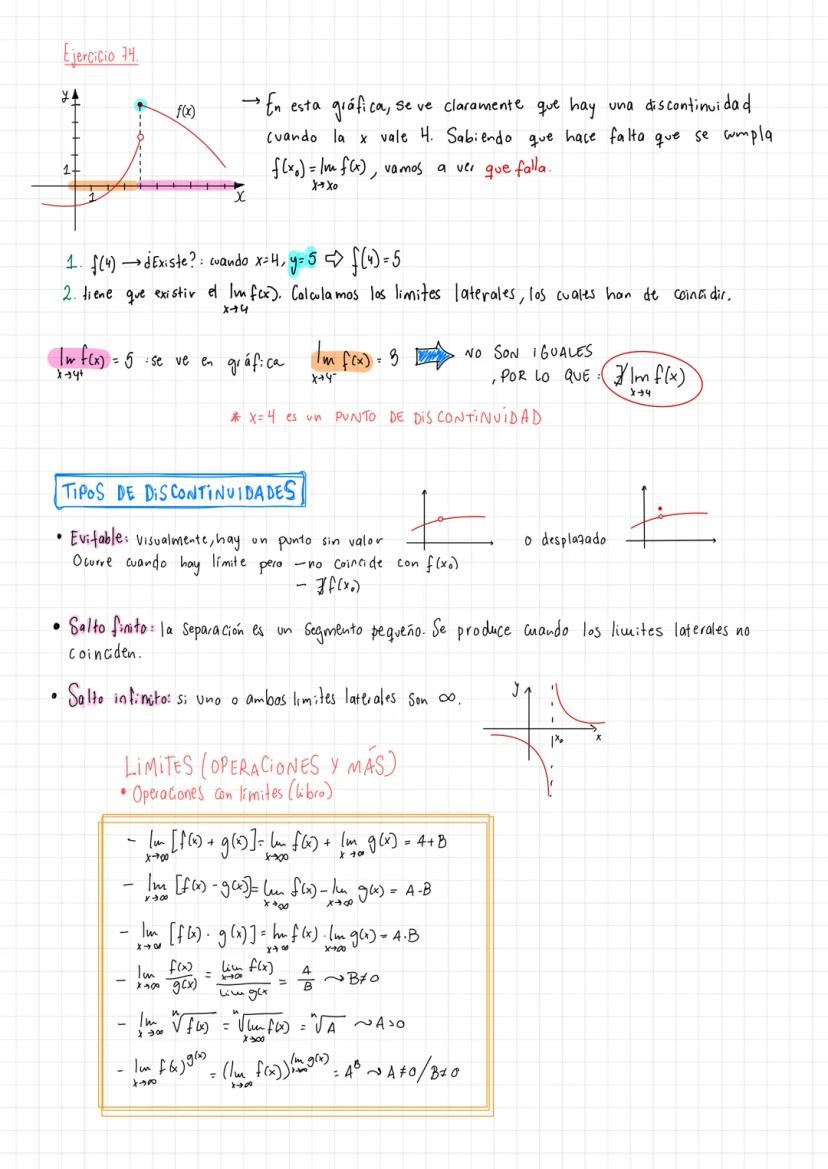
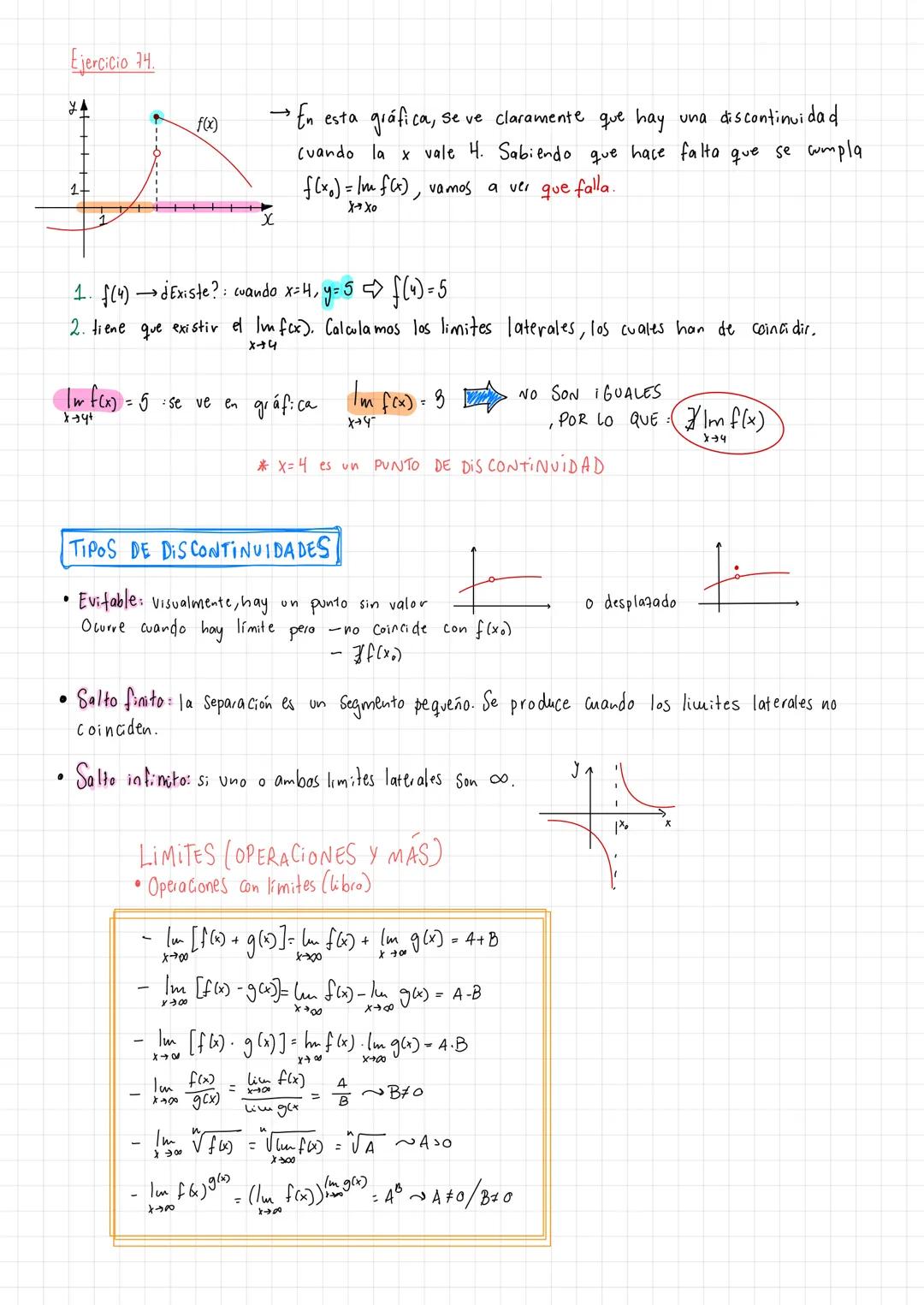
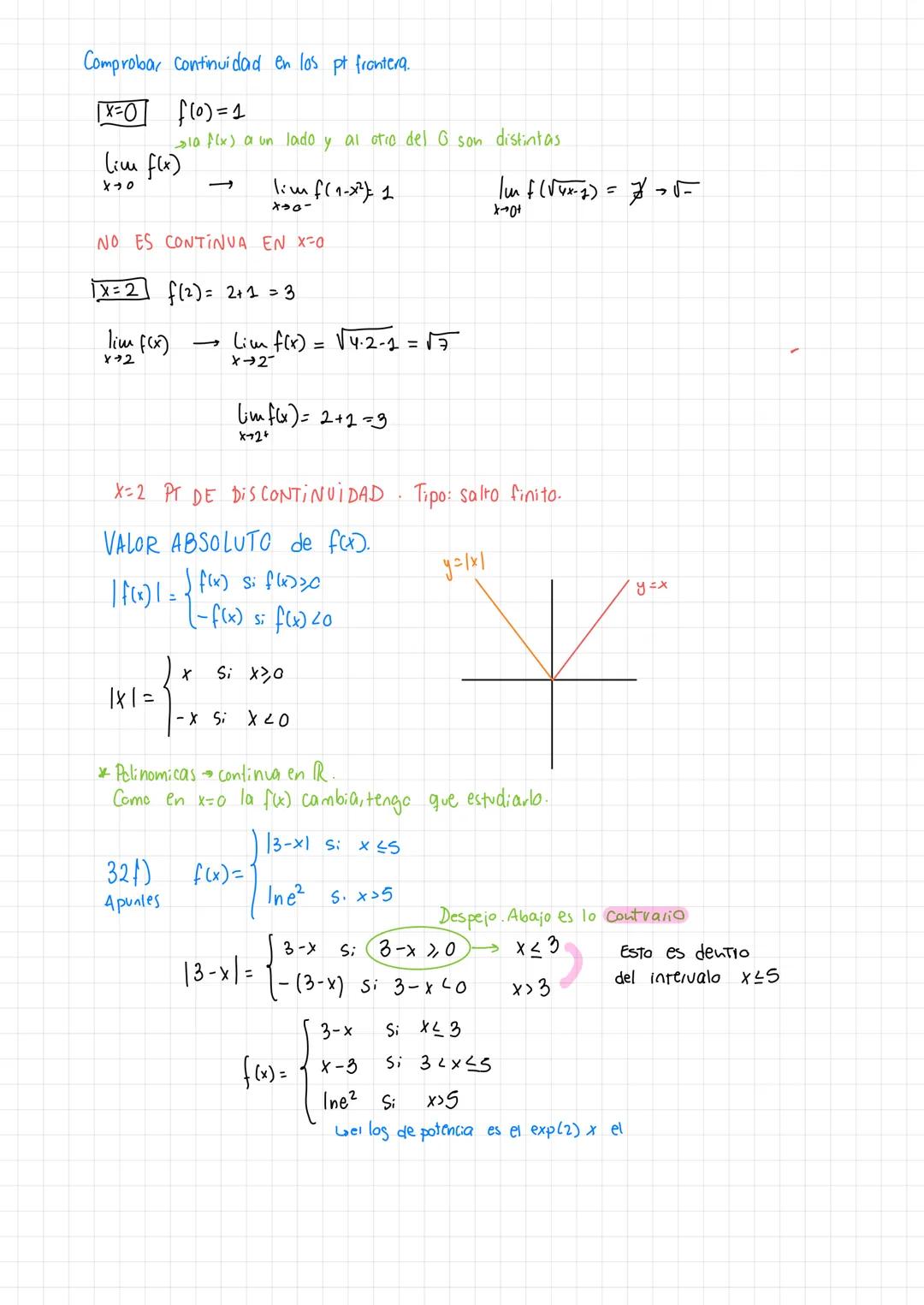
• Detailed explanations of tipos de discontinuidades and function analysis are provided
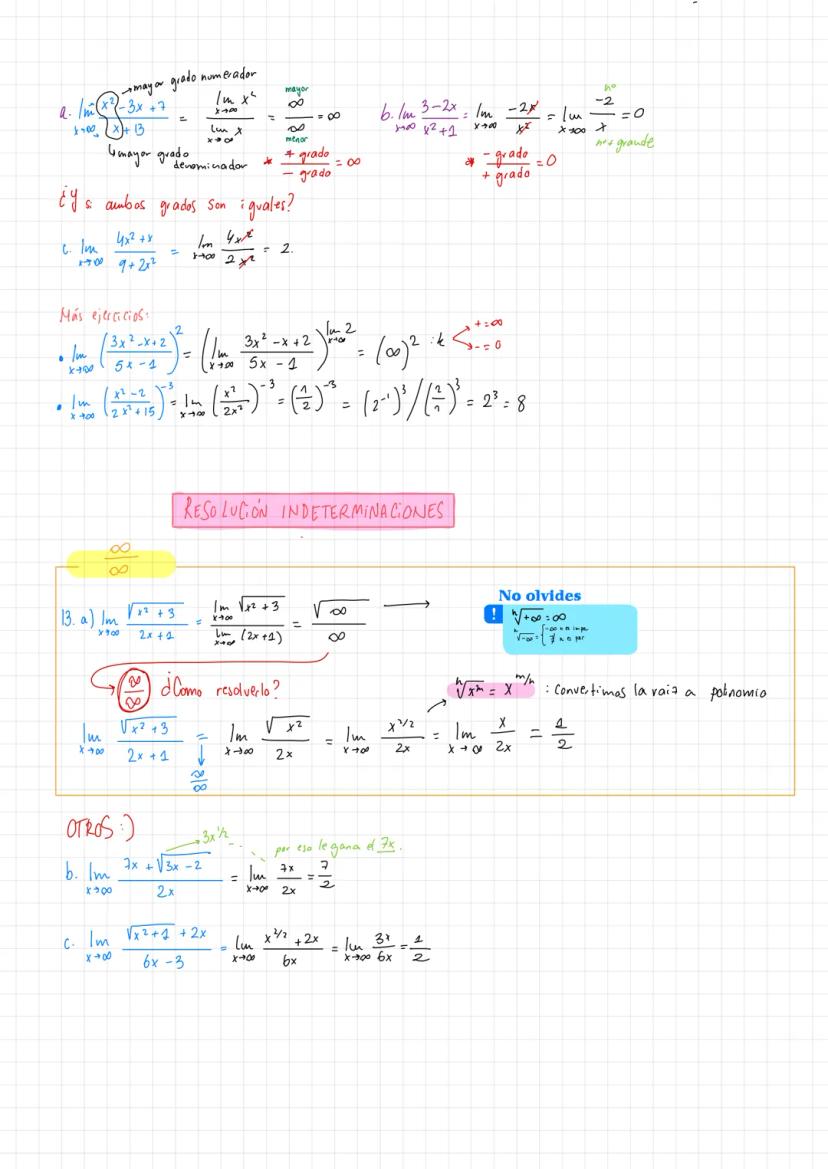
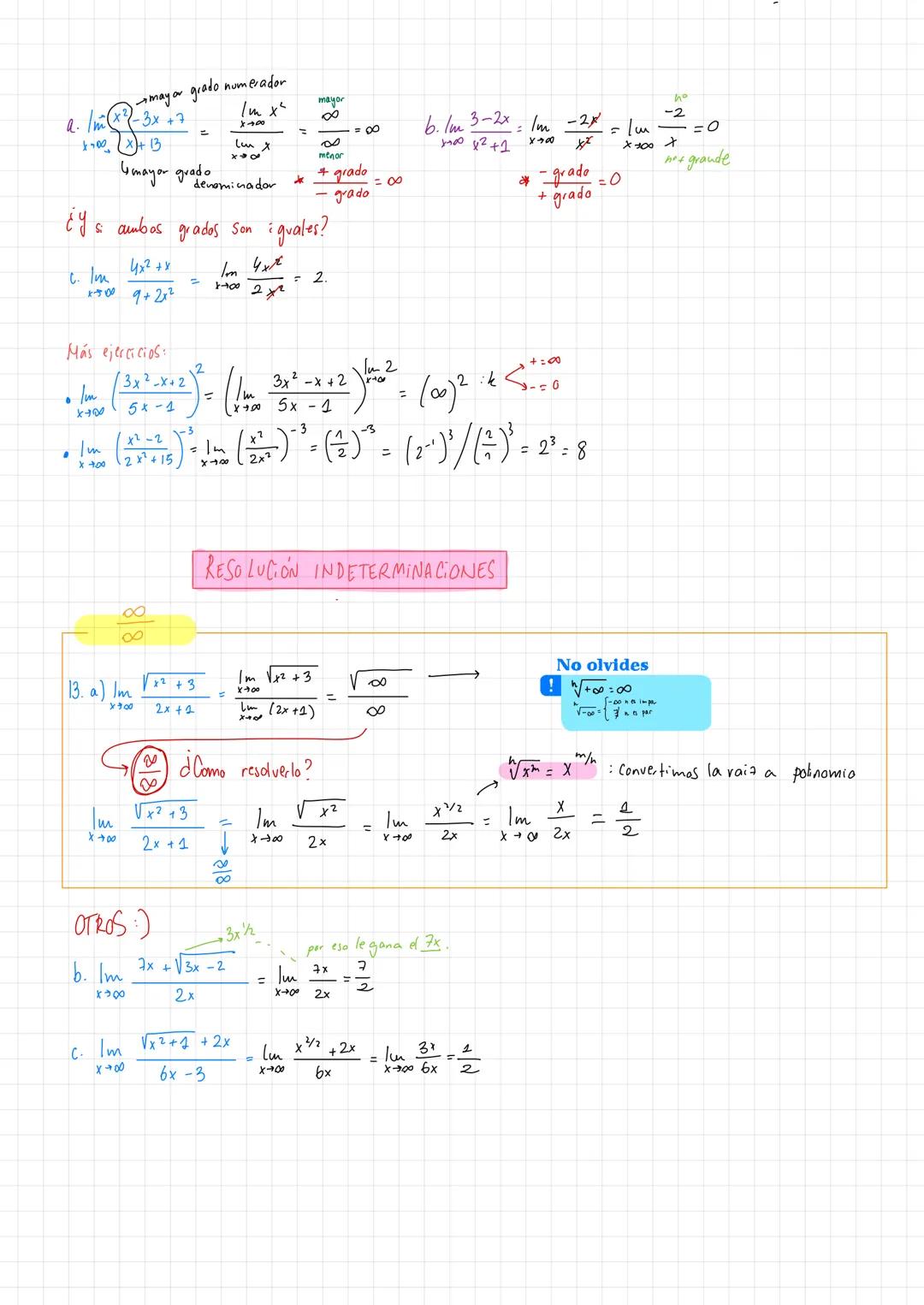
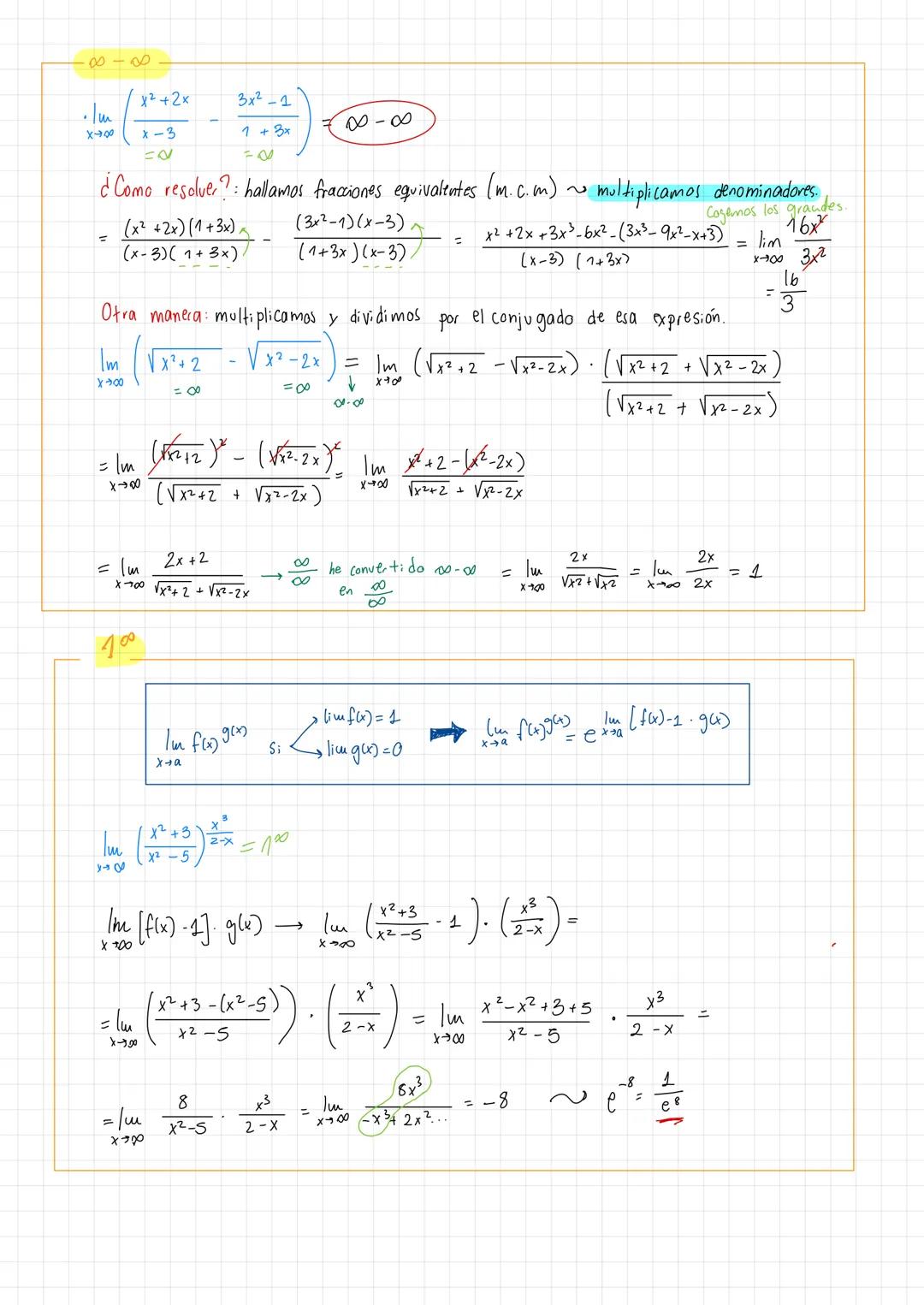
• Examples demonstrate practical applications of límites de funciones racionales ejercicios
• Special focus on puntos de discontinuidad en una gráfica and their analysis